
The graphics processing unit, or GPU, is what renders game graphics on your computer screen. Your gaming experience will be more significant the more powerful your GPU is. GPU congestion is one of the most frequent issues that consumers encounter.
Understanding a GPU bottleneck and how to properly fix it is crucial if you use any GPU-intensive software, such as video editing, gaming, or rendering.
You must understand how to resolve your GPU bottleneck issue because it could affect your computer’s performance and appearance and cause latency. So today, I’m going to discuss what is a GPU bottleneck is, how to repair it, and whether or not you should even try to cure it.
What Is A GPU Bottleneck?
To understand the CPU-GPU bottleneck, you must first understand what a “bottleneck” is. The neck or mouth of a bottle, often known as the bottleneck, determines how much water or other contents a bottle can hold. As a result, the bottleneck symbolizes a junction that slows down traffic.
“Bottleneck” refers to the maximum quantity of data the CPU and GPU can process concurrently. It is, therefore, possible to process fewer data than data waiting to be processed. It indicates that the data processing capacity is insufficient.
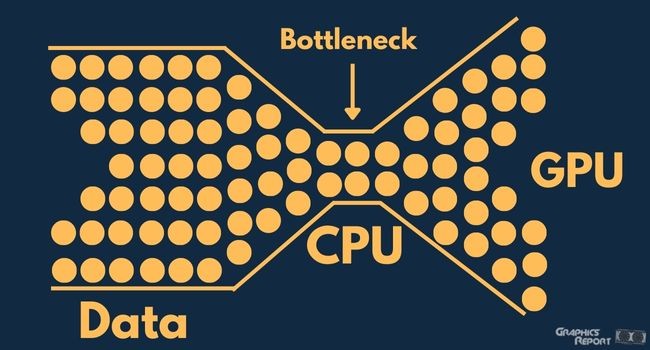
Similarly, the GPU becomes the bottleneck if your CPU is significantly faster than your graphics card. The graphics card, also known as the video card, charges the game’s visual images while the processor handles the game’s actions, audio, and other tasks.
As a result, if the CPU is considerably faster than the GPU, the game will run smoothly, but the screen will be fuzzy because the graphics card is the bottleneck.
How Do Game Bottlenecks Affect Performance?
FPS is the leading gaming performance metric. How many pictures per second can the game render? Today, 60 frames per second are the intended aim, with 30 frames per second considered the least before playability concerns appear.
Every frame a game creates results from a “render pipeline,” which involves a series of processes. If you want to show 30 frames per second, the render pipeline has a 33-millisecond frame restriction.
You have half as much time if you wish to show 60 fps. Some recent games operate at 120fps or more. By doing so, you can render a form in a few milliseconds.
If your CPU can only render 30 frames per second, it doesn’t matter how fast or powerful the GPU is. Also true. Both components must finish their render pipeline jobs inside the time limit, or you’ll have a bottleneck limiting game performance to the slowest.
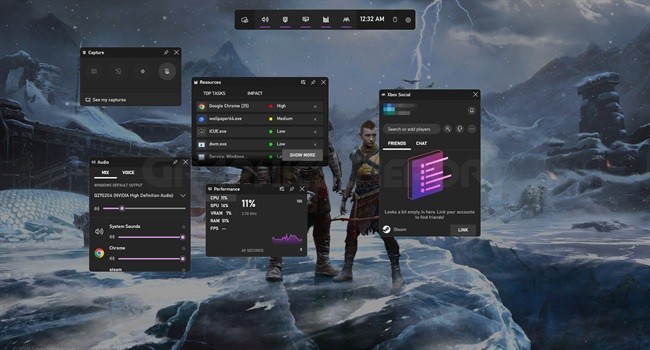
Game bottlenecks are easy to spot. It would be best if you had software to monitor game performance. You can use Win + G to open Windows 10’s (Game Bar) built-in performance monitors or browse for third-party solutions.
Signs of a CPU Bottleneck or GPU Bottleneck
System performance depends on CPU and GPU synchronization—two of your PC’s most important processors. The CPU drives most of your gaming outputs, such as AI and other codes. Game pictures are rendered in high quality by the GPU.
The monitoring system (Game Bar) can find a bottleneck. It’s built into most Windows. It’s opened using Win+G. If this doesn’t work, try MSI Afterburner.
These rules can help you find your system’s bottleneck. Standard rules apply practically everywhere. See If CPU usage is around 100% and GPU usage is low.
Your CPU is the bottleneck since it can’t keep up with the GPU. CPU use should be below 99-100%, and GPU usage should be 100%. The GPU is the problem if you’re not getting the desired frame rate. The abuse of VRAM or RAM can also cause bottlenecks. Some cases have these, but they’re rare.
Here Are Some Solutions For Your Bottleneck Problems
Your CPU or GPU bottleneck problems are simple to address or resolve. To play music with a similar rhythm, it’s crucial to balance out both components’ processing demands. There are various techniques to mitigate the effects of a CPU bottleneck.
These include altering game settings, quitting background processes, and speeding up your RAM and CPU. You may constantly update your CPU if everything else fails to free up more processing power.
Method 1: Increase The Game’s Resolution
Increasing game resolution shifts load from the CPU to the GPU. You can generally accomplish this in the game’s settings. Higher resolution options increase the number of pixels generated by your GPU, which puts additional strain on it.
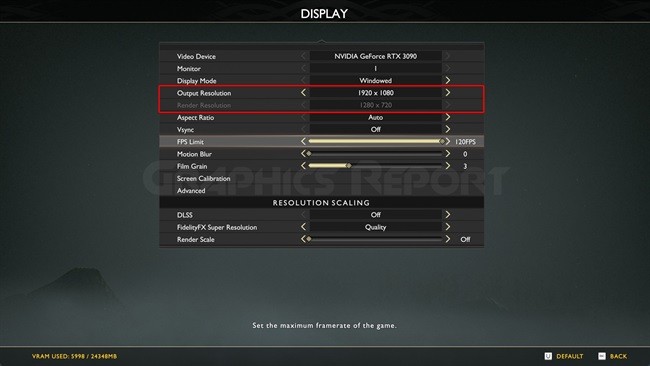
When upgrading the game’s resolution, ensure it’s not higher than your display’s resolution. Your screen’s resolution is under Display Resolution in Display Settings. If you boost a game’s resolution beyond the screen resolution, it will drop your frame rate.
Method 2: Overclock Your CPU
To “overclock” the central processing unit (CPU) means forcing the processor to operate at its maximum possible speed. Which may be faster than the speed officially certified by the processor’s manufacturer. Because of this, the CPU can deal with the data significantly faster without causing any bottleneck issues.
Method 3: Overclock Your RAM
RAM and CPU share a strong working relationship. If you have better RAM, your CPU will receive data more quickly and in a more organized form. Your central processing unit (CPU) will become more efficient and won’t require much effort.

The amount of available RAM directly affects how quickly the CPU can process data. A significant increase in both performance and frames per second can be noted after overclocking the RAM.
Method 4: Upgrade Your CPU
This is crucial if your graphics card and CPU are out of sync. This happens when you replace your GPU with improved graphics without upgrading your CPU. In this situation, boosting your CPU will improve gaming performance, visuals, and processing speed.

Before upgrading, use the GPU comparison tool to check how your new CPU will operate with your GPU. You want to spread the load evenly between the CPU and GPU to avoid CPU bottlenecking the GPU.
Method 5: Close Out Background Applications
If you are experiencing a CPU slowdown, you can alleviate the problem by going into the processes menu and shutting down any extra processes currently operating in the background. That will free up more CPU resources for the game, which can help eliminate bottlenecks. But you should be sure you know which programs can be safely closed.
Method 6: Lower CPU-Intensive Game Settings
Lowering the in-game CPU-bound parameters enables significant improvement and decreases CPU bottleneck problems. These options range from lowering draw distance to increasing vegetation and population density, among others.
Unfortunately, aside from lowering the graphical settings, there aren’t many ways for gamers to solve a GPU bottleneck. On the plus side, a GPU bottleneck is preferable to a CPU bottleneck because it prevents stutters in the game.
Suggested articles:
- What is crossfire and is it worth it in 2023?
- What is g-sync ultimate? (answered today)
- What is nvlink? Is it worth it in 2023?
- What is hardware accelerated GPU scheduling?
- What is HDR technology? & is hdr worth it?
My Final Thoughts On It!
How does GPU bottleneck work? The term “GPU bottleneck” describes a circumstance in which the system’s graphics card performance is sluggish (s). Numerous things can contribute to this, including but not limited to insufficient video memory throughput and excessive heat.
The latter can also happen if too many demanding tasks are active at once on the same hardware, particularly if they are all running under several operating systems or virtual environments.
Your computer’s limiting element should always be the component that will be under the most stress from your anticipated workload.
The other components should provide more than enough assistance, but not too much. Spending excessive money on a component that doesn’t hinder performance could keep you from being able to buy a better component that would genuinely enhance performance.








