
On every computer, there is a video card. The display isn’t working even when the onboard graphics card is activated. Ever pondered the best way to keep it disabled?
This article will discuss how to turn off Windows’ inbuilt graphics hardware. Additionally, you can do so using the BIOS interface. You should utilize the BIOS interface on a laptop or desktop computer to scan and identify the location of the graphics card.
Several methods are available for achieving this. If you have both integrated and dedicated GPUs, I will go into detail on how to do it, whether you should disable it, and how the system would typically handle the switching.
How To Disable Onboard Graphics?
Have you ever had meager frame rates, such as 5 or 10, even after installing a dedicated graphics card? If so, your computer or the application you are using may use the integrated GPU, also known as the built-in graphics card.

Moreover, it is not utilizing your dedicated graphics card. Using the dedicated graphics card, which you most likely paid for, may require turning off the integrated GPU.
Two methods exist for disabling integral graphics. It can be disabled from the BIOS or using Windows Device Manager. It’s also important to note that not all BIOS offer the option to turn off an installed integrated graphics card, so you should act accordingly.
Method #1- Disabling Integrated Graphics Through BIOS
By accessing the basic input/output system (BIOS), administrators can modify the computer’s settings and enable or disable specific devices or peripherals.
The motherboard contains onboard components, such as a graphics chip that allows most modern computers to generate a video at a reasonable cost.
Due to its restrictions, the onboard graphics chip is insufficient for some enterprises. By installing a video card in an expansion slot, you can improve the graphics quality of presentations you make to clients and staff.
However, if you install a card, you may encounter conflicts with the onboard card. In order to avoid these conflicts, it is possible to disable the onboard graphics.
ASUS Motherboard BIOS: Disable Onboard GPU
- The first step in disabling the onboard GPU on an Asus motherboard is to select the advanced tab.
- Next, select System Agent (SA) Configuration.
- Access the Graphic setup menu at this time.
- Select “iGPU Multi-Monitor” from the menu.
- Set its status to disabled.
- After saving the settings, exit BIOS.
By doing this, you will have already turned off your computer’s Asus motherboard’s integrated graphics card.
On MSI Motherboard BIOS; Disable The Onboard GPU
The procedure for turning off the iGPU on an MSI motherboard is primarily the same as for other motherboards:
- You can access the
Integrated Graphics Configuration” menu by selecting “Settings” and then “Advanced”. - Select PEG as the graphics adapter in the Launch menu.
- IGD Multi-Monitor should be found and set to disable.
Disable Onboard GPU On Gigabyte Motherboard BIOS
The procedure is significantly more straightforward if your motherboard is made by AORUS or Gigabyte:
- Go to the Chipset menu
- Look for Integrated Graphics
- Delete it and change it to the disabled.
Some slightly earlier Gigabyte cards had this menu located differently:
- Select the Devices menu at the top.
- Search for the Internal Graphics option
- Which lets you turn it off.
Method #2- Disabling Integrated Graphics Card Through Device Manager
- To accomplish this, click the Windows Taskbar.
- Search the button and type “Device Manager.”
- Control Panel -> Device Manager is another way to reach the device manager.
- To access the “Display Adapters” area, expand the Device Manager Window once it has opened.
- Verify the graphics card that is displayed.
- Click the deactivate option after choosing the integrated graphics card.
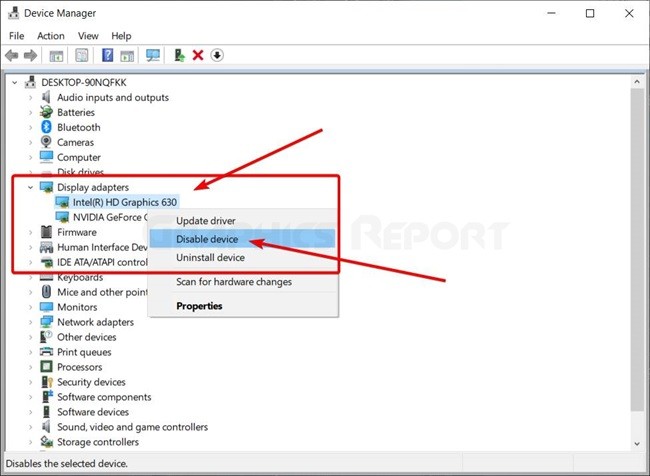
- Do not use the Uninstall (X) button; instead, press the DISABLE button.
- There will be a prompt and some notification. Choose “Yes”.
The screen can then go black for a short period after that. When the display returns, you will see a disabled icon next to the GPU you disabled.
Is It Safe To Disable Integrated Graphics?
It is not advised to turn off the built-in graphics. This is less of a problem with desktop computers because the iGPU is automatically turned off when the dedicated GPU is plugged in.
However, deactivating the integrated graphics on laptops will cause Microsoft Basic Display Driver-based software video processing to take control.

You will notice a significantly decreased performance because Microsoft Basic Display Driver uses the CPU for video processing.
However, it is typically safe to disable the iGPU on a laptop if it is done through the BIOS if you also have an available dedicated GPU installed. Though frequently unnecessary.
What Happens If You Disable All Of Your Graphics Cards?
Your screen will suddenly become black if the leading graphics chip on your computer has been disabled. This scenario arises as a result of inactive hardware that is transmitting visual data to your screen.
Regardless, the issue is software-related and is completely fixable by just resetting the CMOS, which manages the BIOS.
On laptops, your screen won’t go black if you disable both the iGPU and the dedicated GPU (if you have one). Instead, computer-based software rendering will take control.
Video rendering performed by software is much less effective and may cause intolerable performance lags.
On desktop computers, software-based rendering will also take control, but for it to function, your display must be linked to the motherboard’s visual output connector.
Related guides:
- What does AMD’s smart access memory do?
- What is a discrete graphics card? Is it better?
- How to increase VRAM? (tips and tricks)
- Lhr vs non-LHR GPUs (all the differences)
- How to water cool your GPU easily?
My Final Thoughts On It!
You need to know how to distinguish between integrated and dedicated graphics by this point and how to turn off the integrated graphics card in Windows.
There are several reasons you might want to disable your system’s integrated graphics, the first of which is that occasionally the system consumes RAM even though it has a separate graphics card.
You would be wasting some of the system RAM because the machine has built-in video memory. There are occasions when the system, notably Windows, does not recognize all the RAM as usable.
Windows informs you that you only have 7.5 GB of RAM, even when your computer, for instance, has 8 GB. Usable. The screen or display will appear with a reduced resolution, larger icons, and everything else you see before downloading drivers if you disable integrated graphics in device management.








